Sociologists identify different types of families based on how one enters into them
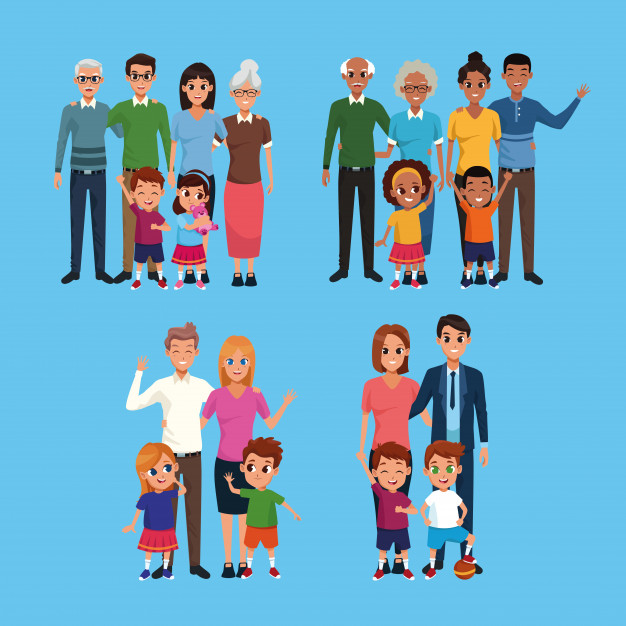
Extended family: All of the family relationships beyond the basic two-generation nuclear or blended family we call it as an Extended Family, which includes relatives beyond nuclear and blended family levels i.e., it consists of cousins, aunts and uncles, grandparents and great grandparents.
Matrifocal family: A matrifocal family consists of a mother and her children. Generally, these children are her biological offspring, although adoption of children is a practice in nearly every society. This kind of family is common where women have the resources to rear their children by themselves, or where men are more mobile than women. As a definition, “a family or domestic group is matrifocal when it is centred on a woman and her children. In this case the father(s) of these children are intermittently present in the life of the group and occupy a secondary place.
Patrifocal family: A patrifocal family consists of a father and his children i.e. a family that is in control by the father, as the head of the family. It is found in societies where men take multiple wives (polygamy or polygyny) and/or remain involved with each for a relatively short time. This type of family is rare from a worldwide perspective, but occurs in Islamic states with considerable frequency. The laws of some Arab nations encourage this structure by allowing a maximum of four wives per man at any given time, and automatic deflection of custody rights to the father in the case of a divorce. In these societies, a man will often take a wife and may conceive a child with her, but after a relatively short time put her out of his harem so he can take another woman without exceeding the quota of four.
Matrilocal family: Matrilocal family is a term referring to the societal system in which a married couple resides with or near the wife’s parents. A woman remains in her mother’s household after reaching maturity and brings her husband to live with her family after marriage. Thus, the female offspring of a mother remain living in (or near) the mother’s house, thereby forming large-clan families, typically consisting of three or four generations living in the same place.Sons, conversely, move out of their natal household after marriage to join their wife’s household.
Patrilocal family/ Virilocal family: Patrilocal family is a society or custom in which a married couple settles with or near the husband’s family. An example of a society that would be described as patrilocal is a society where a woman gets married and moves next door to her husband’s parents. In a patrilocal society, when a man marries, his wife joins him in his father’s home or compound, where they raise their children. These children will follow the same pattern. Sons will stay and daughters will move in with their husbands’ families. Families living in a patrilocal residence generally assume joint ownership of domestic sources. The household is led by a senior member, who also directs the labor of all other members.
Matrilineal family: A matrilineal family is one that follows its ancestry and descendants through the maternal (mother’s) line rather than the paternal (father’s) line. Matrilineal societies are found in various places around the world, such as in parts of Africa, Southeast Asia, and India. In India Matrilineal families are found in the South and in the Northeast. Ex: The Khasis of the Jayantia Hills, the Garos, the Nayars of Malabar, in Kerala etc
Patrilineal family: It is a system in which an individual belongs to his or her father’s lineage. It generally involves the inheritance of property, names, or titles through the male line. In India we generally find such families were the children (irrespective of the sex) are identified by their fathers name and are eligible for the inheritance of their father’s property.
Monogamous family: A monogamous family is one in which the husband and wife are in a monogamous relationship. In other words, they are married to one another exclusively. A monogamous family is based on legal or social monogamy i.e. an individual has only one (official) partner during their lifetime or at any one time (i.e. serial monogamy). This means that a person may not have several different legal spouses at the same time, as this is usually prohibited by bigamy laws, in jurisdictions that require monogamous marriages.
Polygamous family: Polygamy is a marriage that includes more than two partners i.e. having more than one spouse at a time. Polygamy is more well-known in developing countries in Africa and Asia. When a man is married to more than one wife at a time, the relationship is called polygyny; and when a woman is married to more than one husband at a time, it is called polyandry. If a marriage includes multiple husbands and wives, it can be called polyamory, group or conjoint marriage.
Joint family: The joint family or undivided family is an extension of the nuclear family (parents and dependent children), i.e. it is an extended family arrangement and it typically grows when children of one sex do not leave their parents home at marriage but bring their spouses to live with them. A joint family is prevalent throughout the Indian sub continent, particularly in India, consisting of many generations living in the same household, all bound by the common relationship.









When I view your RSS feed it just gives me a page of weird text, may be the problem on my reader? TY for putting this up, it was very helpful and explained tons.
Very interesting subject , regards for putting up.
Thank you
Hiya very cool blog!! Guy .. Excellent .. Superb .. I will bookmark your site and take the feeds also…I’m happy to seek out so many useful info right here in the put up, we need work out extra strategies on this regard, thanks for sharing.
Welcome
Please let me know if you’re looking for a author for your site. You have some really good articles and I think I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d love to write some material for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please send me an e-mail if interested. Thank you!
Welcome
Wonderful post! We are linking to this particularly great article on
our website. Keep up the good writing
.온라인카지노
Welcome